- Equity Theory Of Motivation Pdf Definition
- Equity Theory Of Motivation Pdf Format
- Equity Theory Of Motivation Pdf
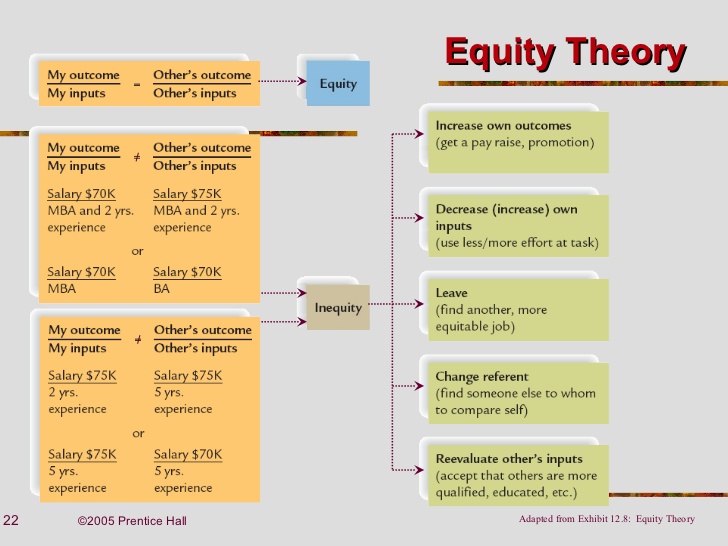
Core of equity is the principle of balance or equity. According to this theory of motivation, an individual’s motivation level is connected with his perception of equity, fairness and justice practiced by management. Equity can be measured by comparing the cost and the reward for each person. This theory was first developed in the year 1960 by J. Stacy Adams. J. Stacy Adam was a workplace and behavioral psychologist, who affirmed that employees seek to maintain balance between the inputs they bring to a job and the outcomes that receive from the job. It is believed that people value fairness and to keep them motivated, fairness is maintained between the co-workers and the organization. Adams suggested that higher the fairness perceived by an employee, higher will be the motivation and vice versa. Common way to see the equity theory at work is when the employee compares the work they do with someone else who gets paid more than them.
Equity theory of motivation tries to address this problem of unequal treatment among employees in a company and its effect on the overall motivation of the employees because slight unequal treatment is present everywhere but when this unequal treatment becomes excessive than it hampers the motivation of the employees in a negative way which can. Equity theory of Motivation 1. EQUITY THEORY Akash Patil CMBA4 2. Introduction to Equity Theory. First developed in 1963 by John Stacey Adams. Employees seek to maintain equity between the inputs that they bring to a job and the outcomes that they receive from it against the perceived inputs and outcomes of others.
This is a comparison between two worker’s A and B. If the output-input of worker A is greater than B, then it is over rewarded, which leads to no motivation. Because he will start thinking that he is getting more money so his efforts towards the job will decrease. When the output-input level of worker A is less than the worker B, it is a situation of Negative Tension State, in which an employee will get motivated to work. Equity is achieved when the output-input relationship of both the workers remains same.
Referents: These are the four comparisons an employee can make.
Self-inside: An employee’s experience in a different position inside his present organization.
Self-outside: An employee’s experience in a situation outside the present organization.
Other-inside: Another employee or group of employees inside the employee’s present organization.
Other-outside: Another employee or employees outside the employee’s present organization.
Inputs:
- Time
- Education
- Experience
- Effort
- Loyalty
- Hard work
- Ability
- Adaptability
- Tolerance
- Determination
Outputs:
- Job Security
- Job Safety
- Recognition
- Reputation
- Responsibility
- Praise
- Employee Benefits
- Sense of achievement
Assumptions of Equity Theory
- This theory indicates that an individual is concerned with what he is getting and also what others are getting in their comparison.
- Employees expect fair and equitable return from their jobs.
- Employees themselves decide what is equitable and fair for them, after comparing them with the other employees.
- Employees who feels that they are being in an inequitable scenario, they will try to distort the input or the output of the company or by quitting the organization.

Importance of the equity theory of motivation
a) Achievement- Through this theory, an employee will feel equitable and fair. So, his motivation will be increased and since the motivation will increase, employee will start working towards his goal more to achieve the target before time and get equally rewarded for it.
b) Diversity- Diversity is the result of workplaces functioning equitably. Diversity means more experience, more perspective and more source material to draw from in brainstorming.
Criticism of the equity theory of motivation
- Since every organization has some structure, so it is not easy for the managers to have equity in the whole organization.
- If managers will keep workplace equity, then it means that there will be no distinction among employees and everything will be same. Since, every employee gets motivation on the basis of salary and other factors and if they remove all these from the organization, motivation among the employees will be removed.
- Financial Solvency- An organization without clearly defined roles means all employees should be equally compensated. In a workplace with total equity, there is no delineation between roles and therefore no distinction that separates management roles from support roles. The result is that all employees would be classified as equal and paid as such, regardless of an employee's actual job function.
Few important topics related Employee motivation
- Motivation Theories
- Methods of motivating employees
- The Needs Theory
- ERG Theory of Motivation
- Acquired Needs Theory
- The Equity theory of Motivation
- Vroom’s Expectancy Theory
- Thorndike's Reinforcement Theory
- Locke’s Goal Setting Theory
- Self Determination
- Cognitive Evaluation Theory
- Reward Systems & Employee Behavior
The core of the equity theory is the principle of balance or equity. As per this motivation theory, an individual’s motivation level is correlated to his perception of equity, fairness and justice practiced by the management. Higher is individual’s perception of fairness, greater is the motivation level and vice versa. While evaluating fairness, employee compares the job input (in terms of contribution) to outcome (in terms of compensation) and also compares the same with that of another peer of equal cadre/category. D/I ratio (output-input ratio) is used to make such a comparison.
| EQUITY THEORY | |
| Ratio Comparison | Perception |
| O/I a < O/I b | Under-rewarded (Equity Tension) |
| O/I a = O/I b | Equity |
| O/I a > O/I b | Over-rewarded (Equity Tension) |
Negative Tension state: Equity is perceived when this ratio is equal. While if this ratio is unequal, it leads to “equity tension”. J.Stacy Adams called this a negative tension state which motivates him to do something right to relieve this tension. A comparison has been made between 2 workers A and B to understand this point.
Referents: The four comparisons an employee can make have been termed as “referents” according to Goodman. The referent chosen is a significant variable in equity theory. These referents are as follows:
| Self-inside: An employee’s experience in a different position inside his present organization. |
| Self-outside: An employee’s experience in a situation outside the present organization. |
| Other-inside: Another employee or group of employees inside the employee’s present organization. |
| Other-outside: Another employee or employees outside the employee’s present organization. |
An employee might compare himself with his peer within the present job in the current organization or with his friend/peer working in some other organization or with the past jobs held by him with others. An employee’s choice of the referent will be influenced by the appeal of the referent and the employee’s knowledge about the referent.
Moderating Variables: The gender, salary, education and the experience level are moderating variables. Individuals with greater and higher education are more informed. Thus, they are likely to compare themselves with the outsiders. Males and females prefer same sex comparison. It has been observed that females are paid typically less than males in comparable jobs and have less salary expectations than male for the same work. Thus, a women employee that uses another women employee as a referent tends to lead to a lower comparative standard. Employees with greater experience know their organization very well and compare themselves with their own colleagues, while employees with less experience rely on their personal experiences and knowledge for making comparisons.
Choices: The employees who perceive inequity and are under negative tension can make the following choices:
| Change in input (e.g. Don’t overexert) |
| Change their outcome (Produce quantity output and increasing earning by sacrificing quality when piece rate incentive system exist) |
| Choose a different referent |
| Quit the job |
| Change self perception (For instance - I know that I’ve performed better and harder than everyone else.) |
| Change perception of others (For instance - Jack’s job is not as desirable as I earlier thought it was.) |
Assumptions of the Equity Theory
- The theory demonstrates that the individuals are concerned both with their own rewards and also with what others get in their comparison.
- Employees expect a fair and equitable return for their contribution to their jobs.
- Employees decide what their equitable return should be after comparing their inputs and outcomes with those of their colleagues.
- Employees who perceive themselves as being in an inequitable scenario will attempt to reduce the inequity either by distorting inputs and/or outcomes psychologically, by directly altering inputs and/or outputs, or by quitting the organization.
| ❮ Previous Article | Next Article ❯ |
Equity Theory Of Motivation Pdf Definition
